Human Resources Best Practices
Define Recruitment: Meaning, Process, and Importance
The Mintly Team
May 05, 2025Recruitment is a fundamental concept in the world of business and human resources. It shapes the workforce of any organization, determining not only who gets hired but also how companies grow, innovate, and compete. Despite its central role, many people only have a vague idea of what recruitment actually means.
This blog post will define recruitment, break down its process, and explain why it is more important than ever in today’s fast-changing job market.
What Does Recruitment Mean?
Recruitment is the process by which organizations find and attract suitable candidates to fill job openings. The main goal is to identify people who have the right skills, experience, and attitude to help the company achieve its objectives. Recruitment isn’t just about filling vacancies—it’s about finding the best possible fit between the organization’s needs and a candidate’s abilities.
Let’s say you are joining Recruitment Company. It is hard to define recruitment when it covers many functions within the organization. Some companies use words as People Team, Staffing Teams, HR Teams.
In simple terms:
Recruitment means searching for potential employees and encouraging them to apply for jobs within an organization.
Why Is Recruitment Important?
Recruitment is crucial for several reasons:
- Building a Skilled Workforce
The quality of an organization’s employees directly impacts its performance. Effective recruitment ensures that only qualified candidates are chosen, which leads to higher productivity and innovation. - Reducing Turnover
Good recruitment practices increase the likelihood that new hires will be a good fit, reducing early turnover and saving costs related to rehiring and retraining. - Maintaining Organizational Culture
Recruitment helps preserve or shape a company’s culture by bringing in people whose values align with those of the business. - Fueling Growth
As businesses expand, they need more staff. Recruitment enables organizations to scale by finding talent quickly and efficiently.
The Recruitment Process: Step by Step
Recruitment is not a single event but a multi-stage process. Here’s how most organizations approach it:
1. Identifying the Need
Everything starts when a gap is identified—maybe someone leaves, or perhaps the company is growing. HR works with managers to understand what role needs filling and what skills are required.
2. Creating a Job Description
The next step is writing a clear job description. This document outlines:
- Responsibilities of the role
- Required skills and qualifications
- Desired experience
- Any special attributes (e.g., teamwork, leadership)
A well-written job description attracts the right candidates and repels those who aren’t suitable.
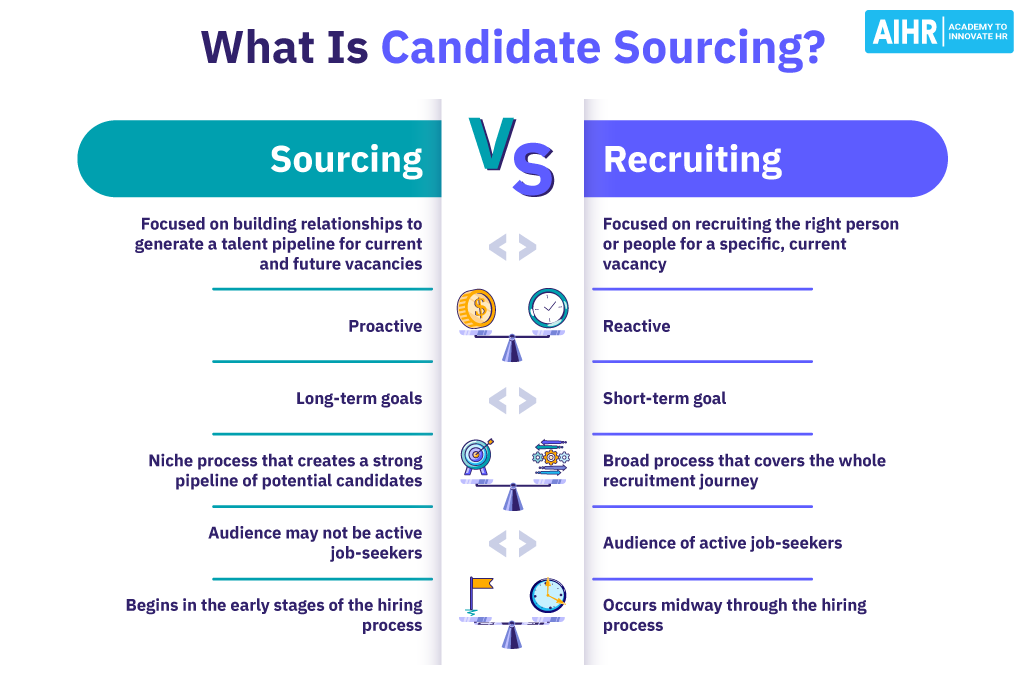
3. Sourcing Candidates
This is where the search begins. Companies use several methods:
- Internal Recruitment: Promoting or transferring existing staff
- External Recruitment: Attracting people from outside through advertisements, job boards, recruitment agencies, social media, campus drives, employee referrals, and more
4. Screening Applications
Once applications start coming in, HR screens them to filter out unqualified candidates. This may involve:
- Reviewing resumes/CVs
- Cover letters
- Online assessments
- Phone screenings
5. Interviewing
Shortlisted candidates are invited to interviews. Interview Skills play a major role in Recruitment process. These can be:
- One-on-one
- Panel interviews
- Group interviews
- Video calls (especially for remote roles)
The purpose is to assess skills, experience, cultural fit, and motivation.
6. Testing & Assessment
Some roles require additional testing (e.g., technical tests for programmers or case studies for consultants). These assessments help verify that candidates actually possess the required knowledge or abilities.
7. Reference Checks
Before making an offer, employers often check references to confirm past employment and performance. Background check tools are available online to help you with checking the history of the candidates.
8. Making the Job Offer
If all goes well, the company extends a job offer outlining salary, benefits, work hours, and other terms.
9. Onboarding
Recruitment doesn’t end with an accepted offer. Onboarding helps new hires become productive members of the team by providing training and support during their first weeks or months.
Types of Recruitment
Recruitment comes in different forms depending on business needs:
- Internal Recruitment:
Filling vacancies with current employees through promotions or transfers. - External Recruitment:
Hiring people from outside the company. - Campus Recruitment:
Visiting colleges/universities to hire fresh graduates. - Headhunting/Executive Search:
Targeting highly skilled professionals or executives for senior positions. - Outsourced Recruitment (RPO):
Contracting third-party agencies to handle some or all recruitment functions.
Challenges in Recruitment
Recruitment has never been more complex than it is today. Some common challenges include:
- Talent Shortages: In some industries (like tech or healthcare), it’s hard to find qualified candidates. Every company adapts differently and hiring is totally different according to them. When you are someone joining, to define recruitment may not be answerable in one word.
- High Competition: Many companies are chasing the same top talent.
- Cultural Fit: Skills are important, but so is personality and alignment with company values.
- Diversity & Inclusion: Modern businesses strive for diverse teams but must avoid bias in hiring.
- Remote Work: The rise of remote jobs has expanded candidate pools globally but also increased competition.
- Technology: HR tech like applicant tracking systems (ATS), AI-driven assessments, and video interviews have changed how recruitment works—making it faster but sometimes less personal.
Best Practices for Effective Recruitment
To recruit successfully, organizations should:
- Define Clear Requirements: Know exactly what skills and traits are needed.
- Use Multiple Channels: Don’t rely on just one source—explore job boards, networking events, social media, etc.
- Invest in Employer Branding: A strong employer brand attracts better talent.
- Streamline Processes: Make application and hiring steps smooth and candidate-friendly.
- Focus on Diversity: Broaden your search to reach underrepresented groups.
- Provide Feedback: Keep candidates informed throughout the process.
- Leverage Technology Wisely: Use automation for repetitive tasks but keep a human touch where it matters.
The Future of Recruitment
Recruitment is evolving rapidly thanks to technology and changing expectations. To Define a Recruitment process, we need to also measure the impact of tech and process adaptation.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI can help screen resumes faster and even conduct initial interviews, but human judgment remains essential.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Analytics are being used to predict which candidates will succeed.
- Remote & Hybrid Roles: Companies can now hire from anywhere, opening up new possibilities and challenges.
- Focus on Experience: Candidate experience matters—poor communication or long waits can damage a brand’s reputation.
- Continuous Learning: Recruiters need to keep learning new tools and trends to stay effective.
Final Thoughts
Recruitment is much more than just filling open positions. You can’t just define recruitment in simple one word. It’s about building the future of an organization by finding the right people at the right time. From identifying needs to onboarding new hires, recruitment touches every aspect of business success.
As workforces become more diverse and technology transforms how we hire, mastering recruitment is now a key competitive advantage for any forward-thinking company.
Whether you’re a business owner, HR professional, or job seeker, understanding recruitment will help you navigate the modern workplace with confidence—and ensure that you’re always prepared for what comes next.
All Tags
Loading...
Loading...