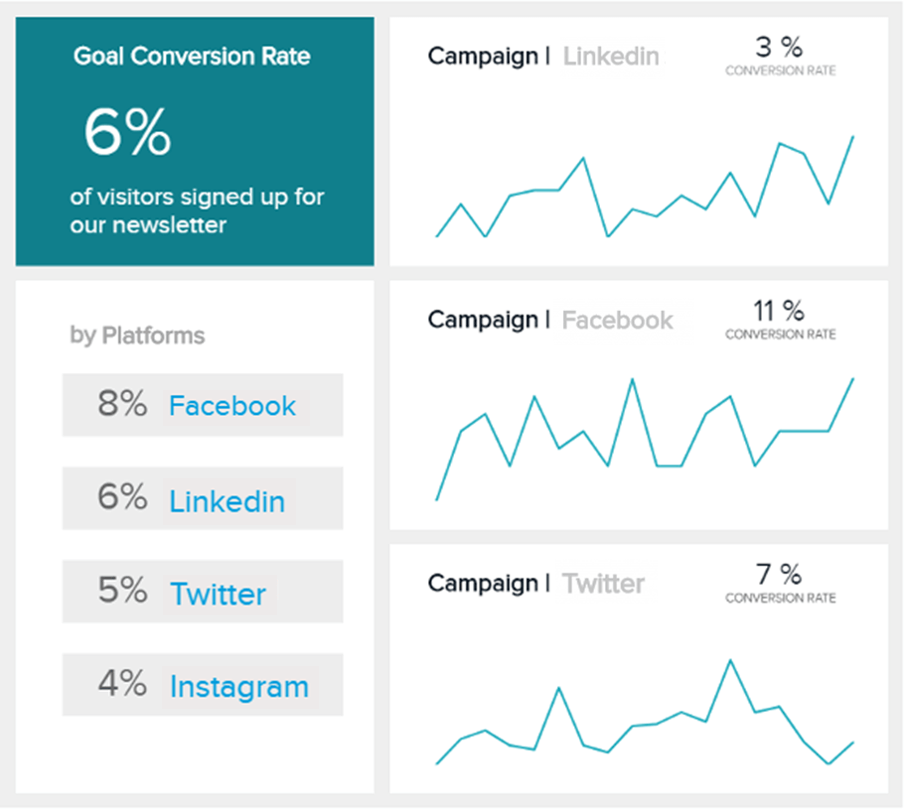
Productivity metrics are essential tools for measuring the efficiency and effectiveness of various processes within a business or organization. By tracking these metrics, managers and team members can identify areas that need improvement and recognize where things are going well. Let’s explore some of the most commonly used productivity metrics across different industries.
Output-Based Metrics
1. Units Produced
One of the most straightforward productivity metrics is the number of units produced within a given time frame. This could refer to physical items in manufacturing or completed tasks in a service-based setting.
2. Sales Revenue
For businesses focused on sales, revenue is a clear indicator of productivity. Tracking sales revenue over time helps in assessing how effectively a sales team converts leads into purchases.
3. Customer Transactions
The number of transactions with customers, such as sales, service calls, or checkouts, can indicate the productivity of a team in handling customer interactions and processing work efficiently.
Time-Based Metrics
4. Cycle Time
Cycle time measures the time it takes to complete a business process from start to finish. This metric is crucial for identifying bottlenecks and streamlining operations.
5. Turnaround Time
Closely related to cycle time, turnaround time focuses on the time taken to respond to customer requests or orders, which is vital for customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Efficiency Metrics
6. Efficiency Ratio
This ratio compares the output (usually in revenue or units) to the input (often in terms of labor hours or cost). A higher ratio indicates better efficiency.
7. Capacity Utilization
This metric measures how close a business is to operating at full capacity. It’s calculated by dividing the actual output by the potential output if resources were fully utilized.
Quality Metrics
8. Error Rates
Error rates are critical in industries where precision is vital. They help in monitoring the number of defective products or mistakes made during a process.
9. First Pass Yield
First pass yield refers to the percentage of products or services that meet quality standards without requiring rework, indicating the efficiency of production and quality control processes.
Financial Metrics
10. Profit Per Employee
To assess how much profit each employee contributes, this metric divides total profit by the number of employees. It can provide insights into the overall financial productivity of a workforce.
11. Return on Investment (ROI)
ROI measures the gain or loss generated on an investment relative to the amount of money invested. It is fundamental for evaluating the efficiency of different investments.
Labor Productivity Metrics
12. Revenue Per Employee
This metric divides total revenue by the number of employees, offering an understanding of how effectively a company leverages its human resources to generate income.
13. Labor Productivity Ratio
The labor productivity ratio calculates output (such as goods produced) per labor hour, highlighting how efficiently labor time is used within the production process.
Customer-focused Metrics
14. Net Promoter Score (NPS)
NPS assesses customer satisfaction and loyalty by measuring how likely customers are to recommend a product or service to others.
15. Customer Retention Rate
This metric tracks how well a business maintains its customer base over time, which is essential for long-term success and profitability.
Project Management Metrics
16. Schedule Adherence
Schedule adherence measures how closely projects or tasks follow their planned timelines, which is crucial for meeting deadlines and maintaining project momentum.
17. Milestone Achievement Rate
Tracking the rate at which project milestones are achieved helps in assessing progress and identifying potential delays early in the project lifecycle.
Employee Engagement Metrics
18. Employee Satisfaction Index
An engaged workforce is often more productive. This index measures employee satisfaction levels through surveys and feedback mechanisms.
19. Absenteeism Rate
Frequent absences can be a sign of low engagement or workplace issues, and tracking this rate can help in addressing these problems proactively.
Innovation Metrics
20. Number of New Products Developed
In industries where innovation drives growth, the number of new products or services developed is a telling productivity metric.
21. Time to Market
How quickly a company can move from product conception to market availability is crucial for staying competitive and capitalizing on new opportunities.
Application of Productivity Metrics
One primary application of productivity metrics is in the manufacturing sector. Metrics such as units produced per labor hour allow companies to measure the output relative to the human resources employed. By analyzing this data, managers can identify bottlenecks in production processes, assess the performance of workers, and determine areas where improvements can be made – be it through training, process optimization, or technological upgrades.
In the realm of software development, productivity metrics might include lines of code written per day or function points completed per iteration. These measurements help in tracking progress, forecasting project timelines, and allocating resources efficiently. However, a key consideration in such creative fields is ensuring that productivity metrics are balanced with quality assurance indicators to prevent a decline in the quality of work due to a narrow focus on quantity.
Service industries also apply productivity metrics, such as the number of customers served per employee or average resolution time for customer service inquiries. These metrics are crucial for maintaining high levels of customer satisfaction while managing workforce efficiency.
Furthermore, productivity metrics are instrumental in strategic decision-making. For instance, return on investment (ROI) is a vital metric that helps businesses assess the profitability of their investments relative to the cost incurred. By using ROI and other financial productivity metrics, organizations can make informed decisions about where to invest their capital to maximize returns.
Additionally, in the digital age, data analytics tools have enabled the tracking of employee productivity through various software applications. Such tools can provide real-time analytics on employee performance, time management, and project completion rates.
Overall, the application of productivity metrics is diverse and industry-specific, but the core goal remains constant: to enhance performance and drive growth by making informed decisions based on quantifiable data.
Application of Productivity Metrics
In the realm of software development, productivity metrics might include lines of code written per day or function points completed per iteration. These measurements help in tracking progress, forecasting project timelines, and allocating resources efficiently. However, a key consideration in such creative fields is ensuring that productivity metrics are balanced with quality assurance indicators to prevent a decline in the quality of work due to a narrow focus on quantity.
Service industries also apply productivity metrics, such as the number of customers served per employee or average resolution time for customer service inquiries. These metrics are crucial for maintaining high levels of customer satisfaction while managing workforce efficiency.
Furthermore, productivity metrics are instrumental in strategic decision-making. For instance, return on investment (ROI) is a vital metric that helps businesses assess the profitability of their investments relative to the cost incurred. By using ROI and other financial productivity metrics, organizations can make informed decisions about where to invest their capital to maximize returns.
Additionally, in the digital age, data analytics tools have enabled the tracking of employee productivity through various software applications. Such tools can provide real-time analytics on employee performance, time management, and project completion rates.
Conclusion
Productivity metrics are invaluable for businesses looking to optimize their operations and drive growth. By carefully selecting and applying these metrics, organizations can gain insights into their performance, make informed decisions, and continuously improve their efficiency and effectiveness. Whether focusing on output, time, efficiency, quality, financial health, labor, customer satisfaction, project management, employee engagement, or innovation, the right set of productivity metrics can pave the way for success.